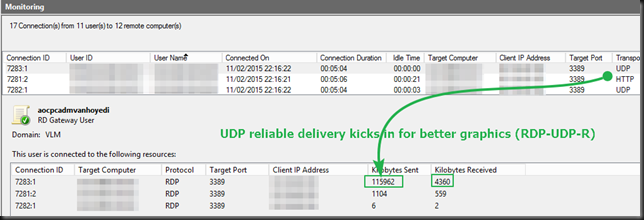
Microsoft and QUIC
If you are interested in Microsoft and QUIC I have some good news for you. Recently a new article, SMB over QUIC Technology | StarWind Blog (starwindsoftware.com) was published. It is the first in a series about what Microsoft is working on in regards to QUIC. While not without some controversy, QUIC does a lot for a number of issues connectivity over “the internet at large” has been dealing with.
- It leverages UDP.
- TLS 1.3 is built into the protocol.
- Reduces RTT during connection & encryption setup.
- Handles and optimizes flow control and loss recovery.
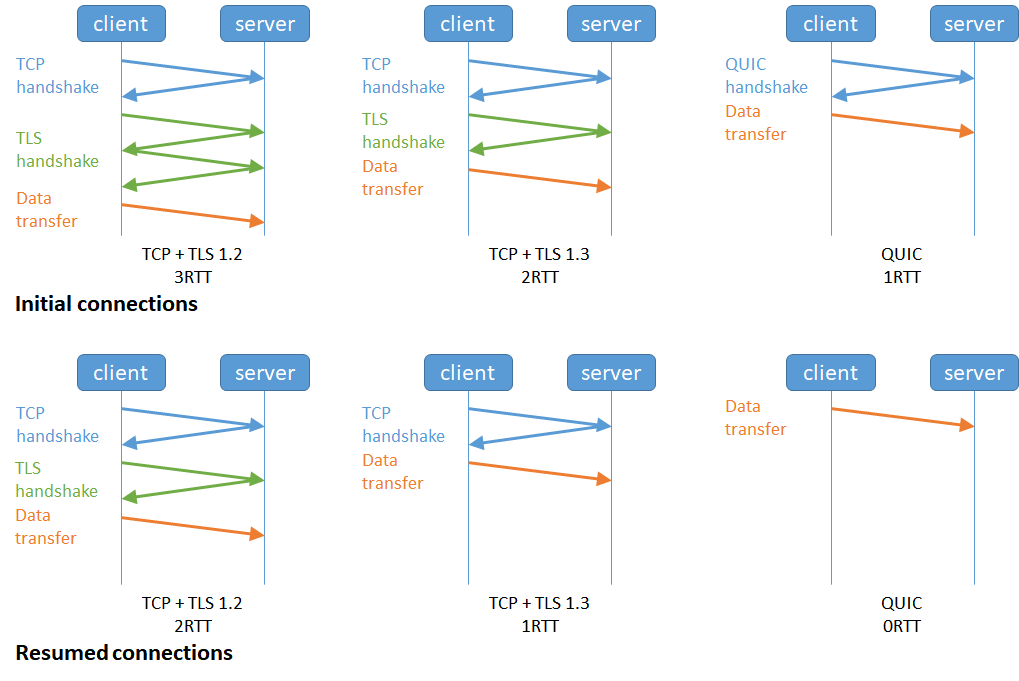
Over the internet, with mobile clients, this is a big deal. Since it is secure by default people really started thinking about where this can be used to improve things for all involved.
I think QUIC is going to be more and more important in the future and this article positions QUIC in the Microsoft ecosystem. So, head over there, read it, and let me know what you think.
TLS 1.3, QUIC, HTTP/3, and SMB 3.1.1 are shaking up things a bit by challenging TCP. Microsoft dropped QUIC into Windows Server 2022 Azure edition. That went into public preview last week and I dove in to the lab to figure out what I can do with it.
As a technologist, I am having a lot of fun testing this out in the lab. Last weekend I was busy with SMB over QUIC and QUIC in IIS. I learned a lot and have made up my mind I can use this in the real world to solve requirements. I will share my findings and musing with you in near the future. But today, start with an introduction in SMB over QUIC Technology | StarWind Blog (starwindsoftware.com).